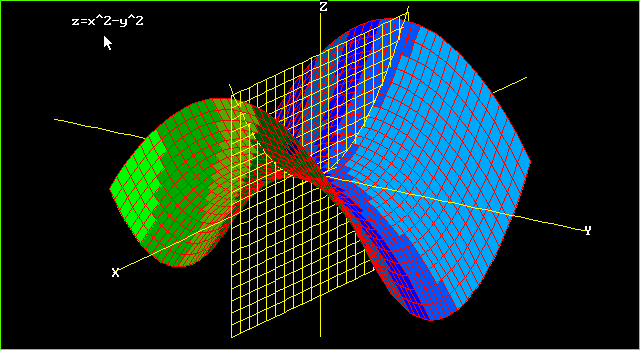
いろいろ z=x^2 y^2 graph 136666-Graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2
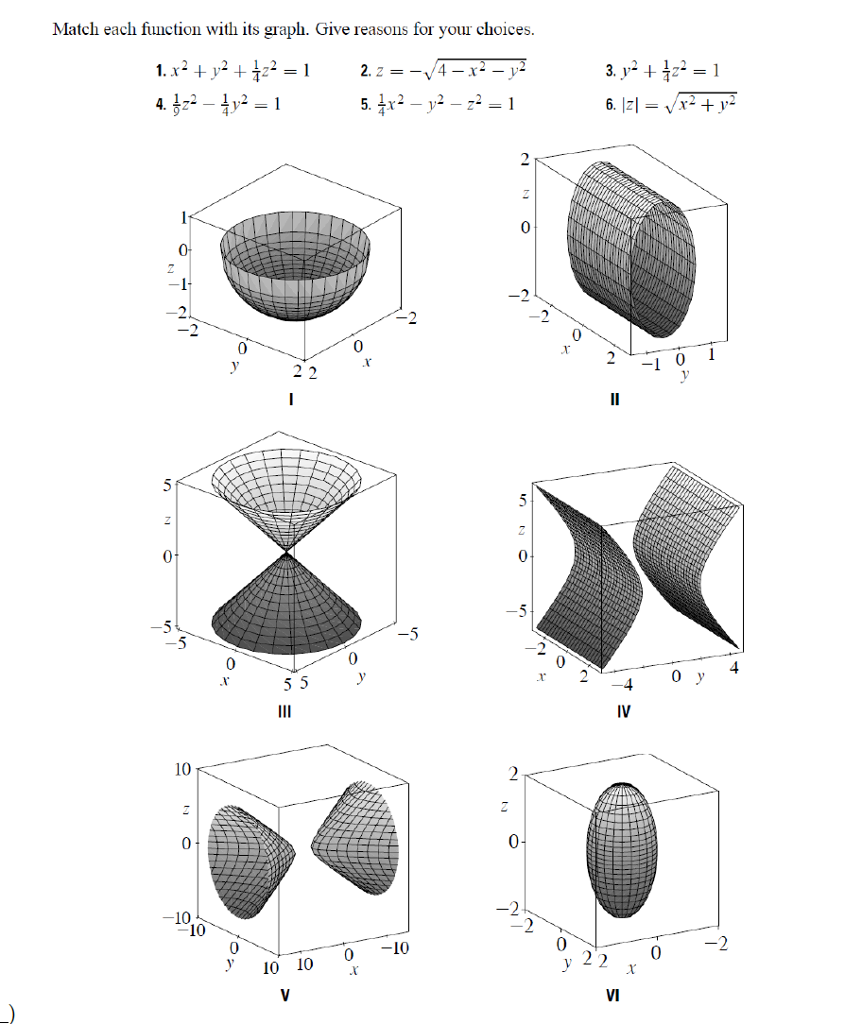
Y 2 Z 2 16 Is This Represents A Circle In 3 Dimensional Space Or 2 Dimensional Space Socratic
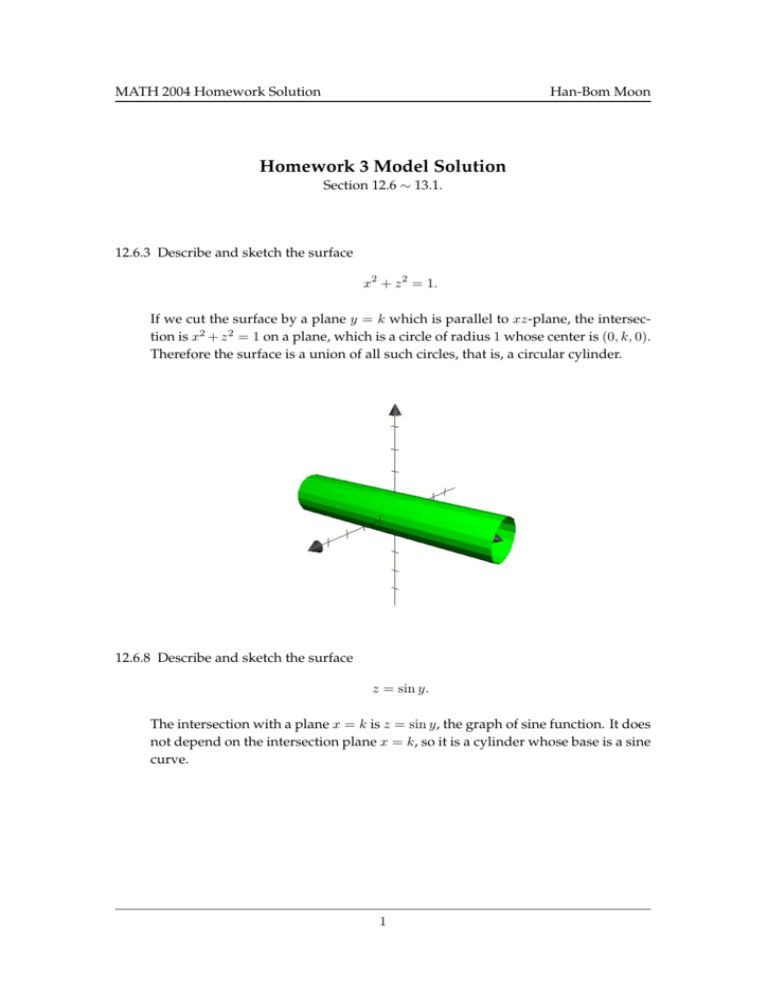
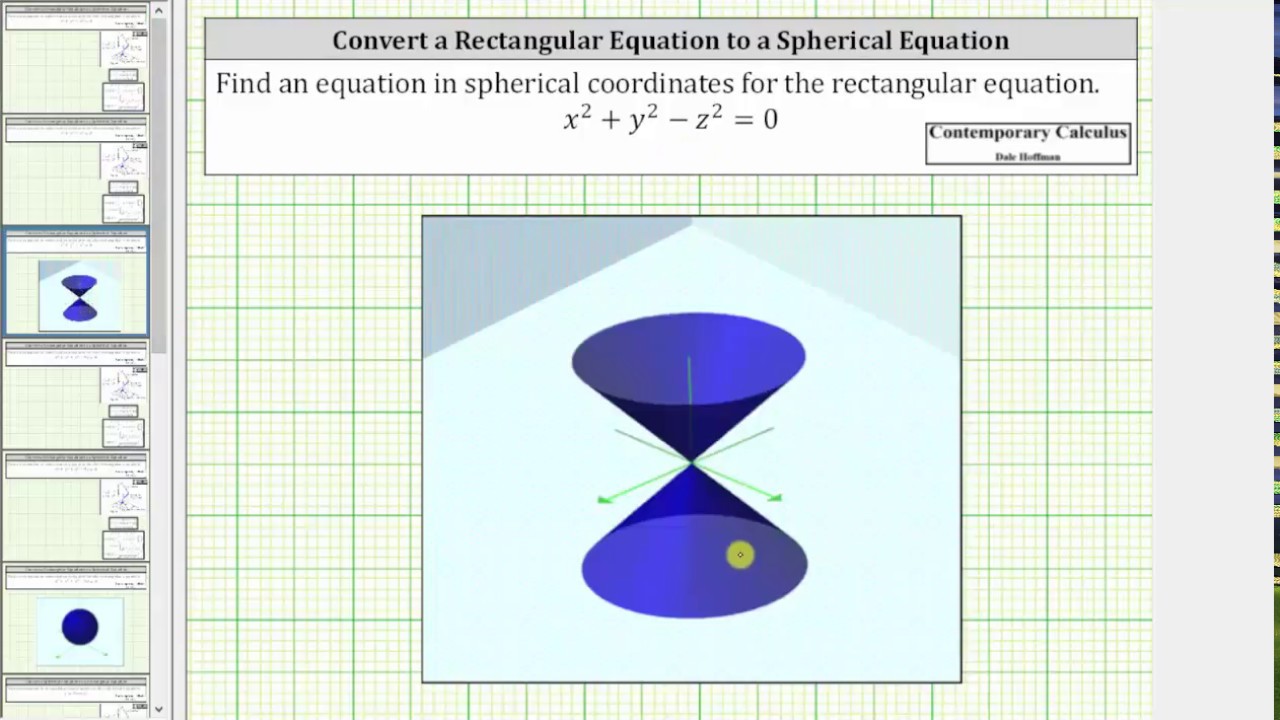
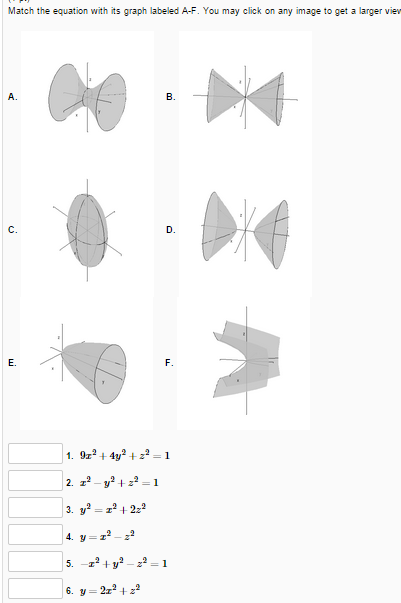
Show activity on this post This figure is the (double) cone of equation x 2 = y 2 − z 2 The gray plane is the plane ( x, y) You can see that it is a cone noting that for any y = a the projection of the surface on the plane ( x, z) is a circumference of radius a with equation z 2 x 2 = a 2 Note that z = y 2 − x 2 is the semicone with z > 0, ie above the plane ( x, y) and z = − y 2 − x 2 is the semiGraph the surface f (x,y,z) = c I have a function f (x,y,z) = x^2 y^2 z^2 and I'd like to graph the surface defined by the equation f (x,y,z) = 1 When I type "S x^2 y^2 z^2 = 1" into the input bar, this works perfectly;
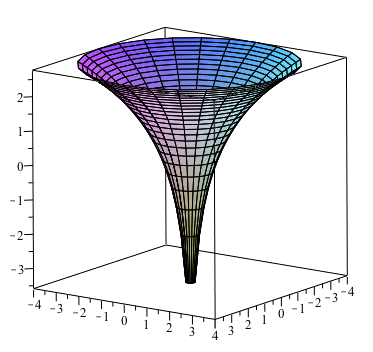
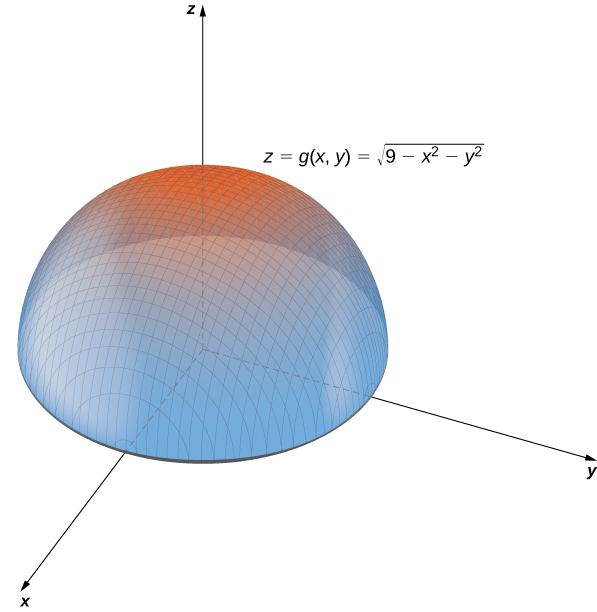
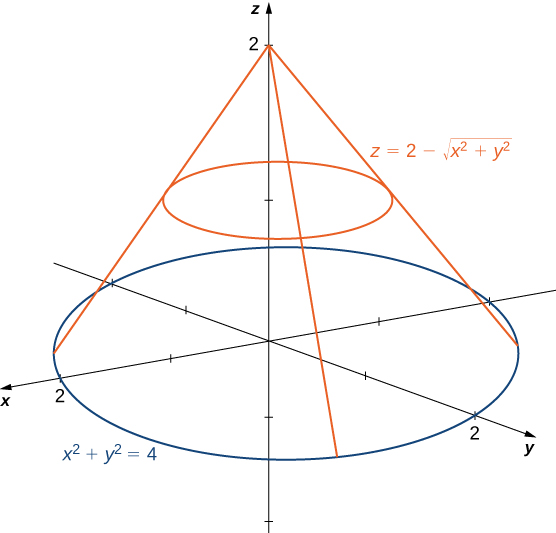
Graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2
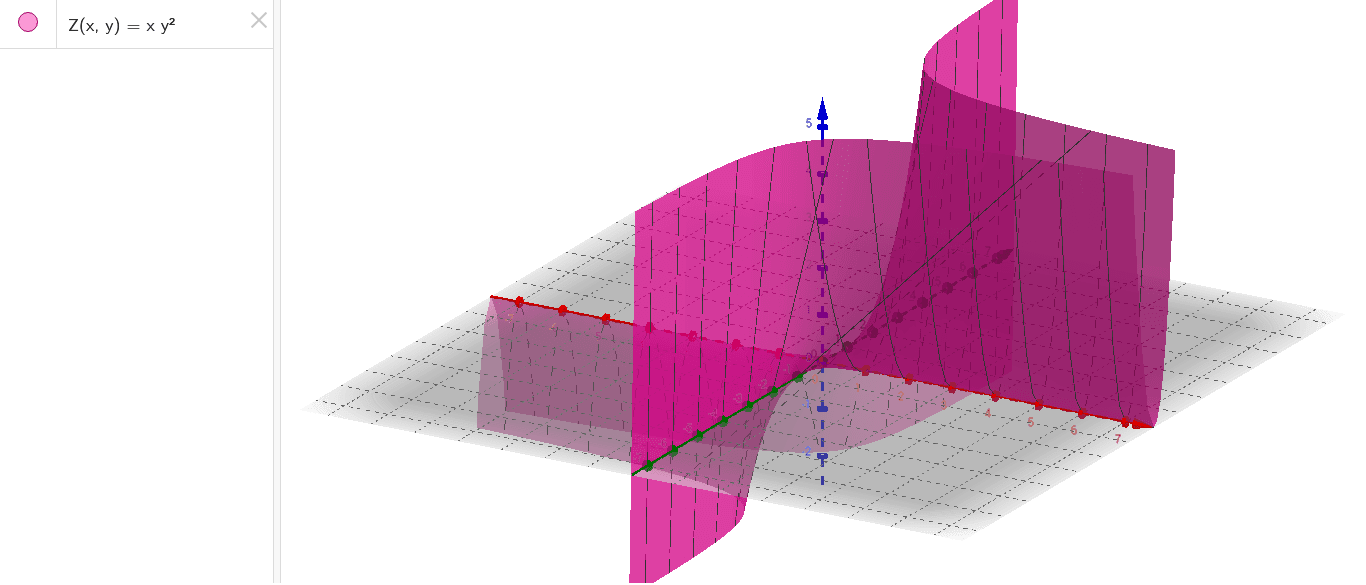
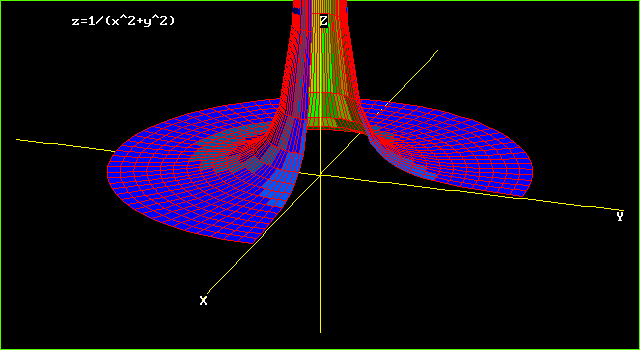
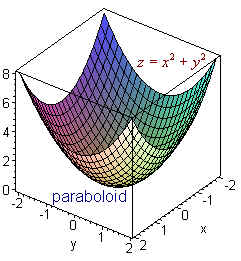
Graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2-When z = x 2 y 2, the trace on y = b is the graph of z = x 2 b 2, while that on x = a is the graph of z = a 2 y 2; Summary Want to find curvature at a point on a 3d graph if the osculating circle is situated in a certain direction I know curvature (k) of a 2 dimensional graph y (x) is equal to y''/ (1 (y')^2)^ (3/2), were y' is the first derivative of y with respect to x, and y'' is the second derivative of y with respect to x
Graphs Of Surfaces Z F X Y Contour Curves Continuity And Limits
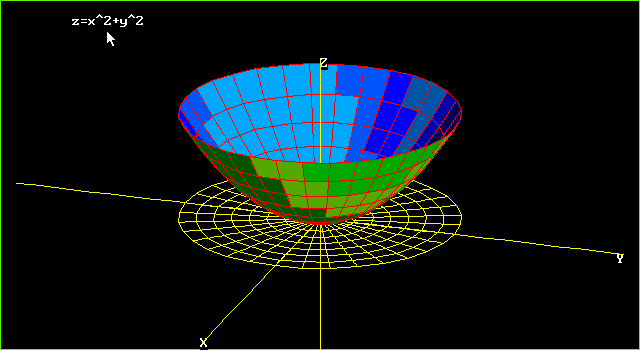
3D and Contour Grapher A graph in 3 dimensions is written in general z = f(x, y) That is, the z value is found by substituting in both an x value and a y value The first example we see below is the graph of z = sin (x) sin (y) It's a function of x and y You can use the following applet to explore 3D graphs and even create your own, using variables x and y Plot z = x^2 y^2 over the interval 4You can clickanddrag to move the graph around If you just clickandrelease (without moving), then the spot you clicked on will be the new center To reset the zoom to the original click on the Reset button Using "a" Values There is a slider with "a =" on it You can use "a" in your formula and then use the slider to change the value of "a
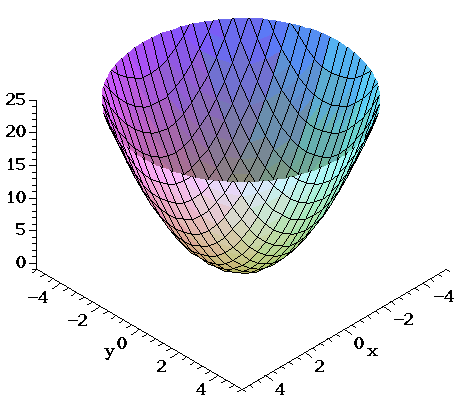
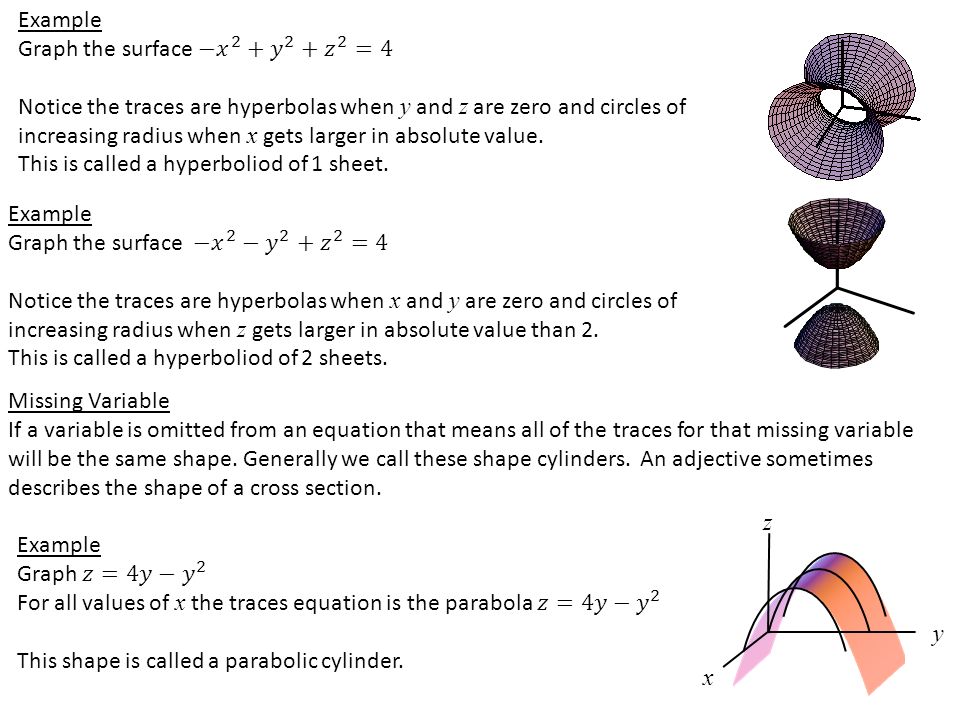
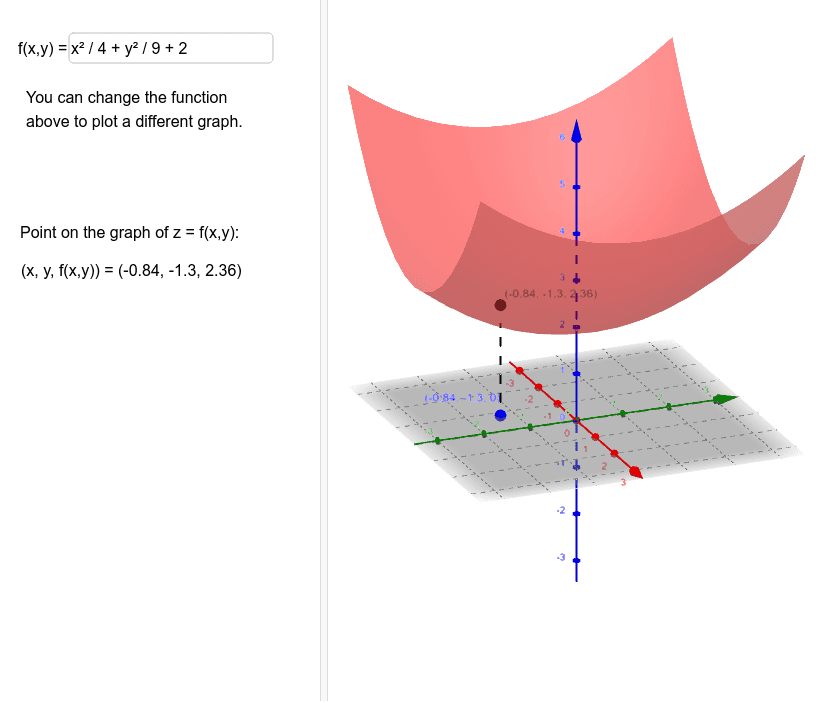
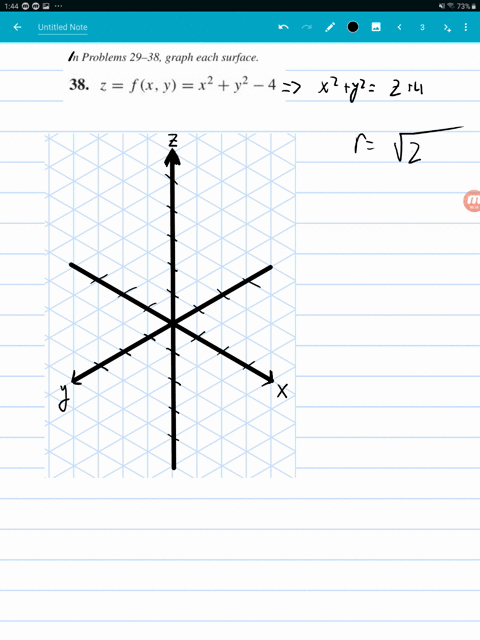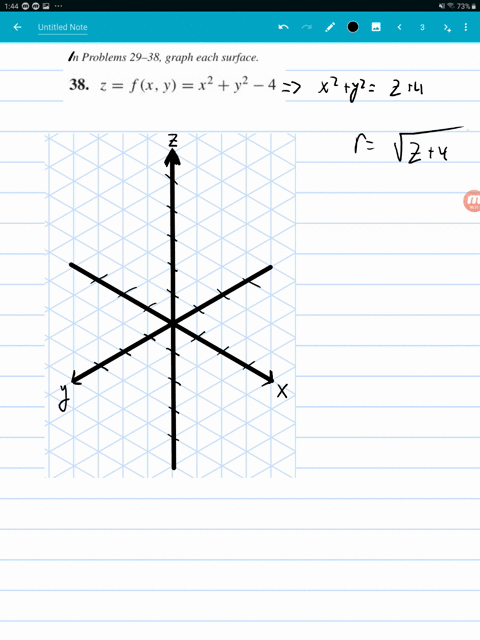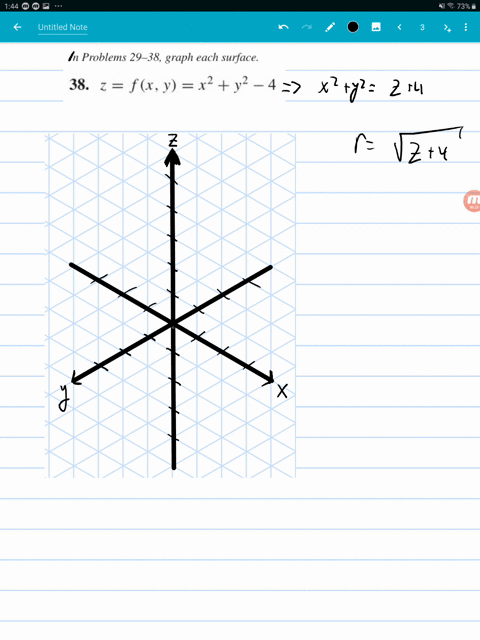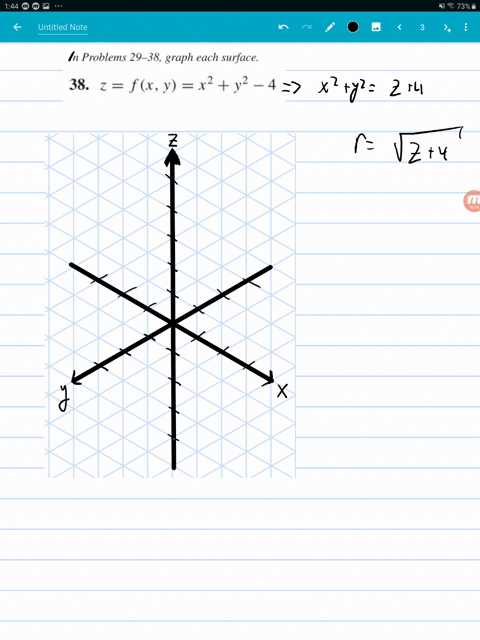
F(x,y,z) = x2 y2 y2 and the constraint is g(x,y,z) = x y z = 6 The vector equation ∇f = λ∇g gives the system 2x = λ, 2y = λ, 2z = λ Therefore, x = y = z, and as the sum is 6, then (x,y,z) = (2,2,2) and the product is 8 16Answer to A) Sketch and identify the surface z = x^2 y^2 B) Find the equation of the intersection z = x^2 y^2 with z = 5 Sketch and identifyThe graph of a function Z = f(X,Y) is the collection of all triples, where the third coordinate, Z, is computed from the first two using the function f For example, the graph of Z=X*XY*Y contains points like (1,1,2), (2,3,13), (1,2,5) since each of these satisfy the equation Specifically, the third coordinates are all obtained from the
Graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2のギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 | ||
 |  | |
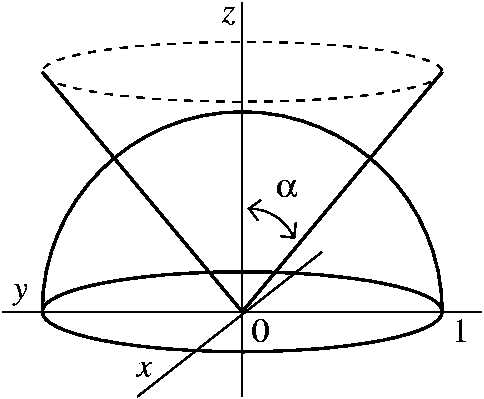 | ||
「Graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | 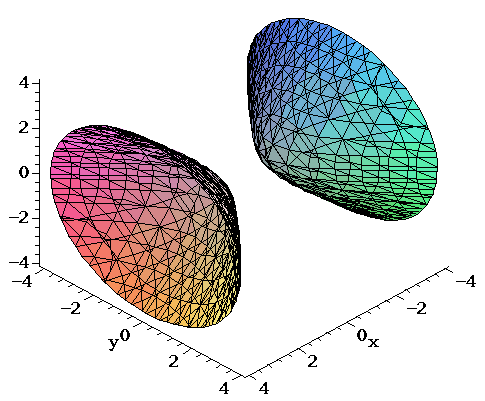 | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「Graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「Graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 | ||
 | ||
「Graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 | ||
「Graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「Graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「Graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「Graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |
Figure 1 Region S bounded above by paraboloid z = 8−x2−y2 and below by paraboloid z = x2y2 Surfaces intersect on the curve x2 y2 = 4 = z So boundary of the projected region R in the x−y plane is x2 y2 = 4 Where the two surfaces intersect z = x2 y2 = 8 − x2 − y2 So, 2x2 2y2 = 8 or x2 y2 = 4 = z, this is the curve at This is a circle with radius 2 and centre i To say abs(zi) = 2 is to say that the (Euclidean) distance between z and i is 2 graph{(x^2(y1)^24)(x^2(y1)^011) = 0 5457, 5643, 184, 371} Alternatively, use the definition abs(z) = sqrt(z bar(z)) Consider z = xyi where x and y are Real
Incoming Term: z sqrt x 2 + y 2 graph, z x 2 + y 2 graph, z x 2 - y 2 graph, graph of z sqrt x 2 + y 2, graph x 2 + y 2 + z 2 1, graph x 2 + y 2 + z 2 2,
コメント
コメントを投稿